Table of contents
Prerequisites !
(Things to have before starting the projects)
AWS Account.
Programmatic access and AWS configured with CLI.
Python3 Installed.
Docker and Kubectl installed.
Code editor (Vscode)
✨Let’s Start the Project ✨
Part 1: Deploying the Flask application locally
Step 1: Clone the code
Clone the code from the repository:
https://github.com/Kritika257/cloud-monitoring-app.git
Step 2: Install dependencies
The application uses the psutil and Flask, Plotly, boto3 libraries. Install them using pip3:
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
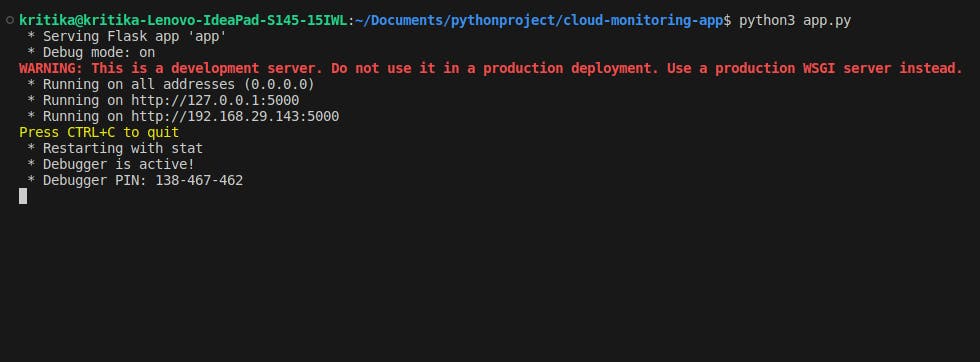
Step 3: Run the application
To run the application, navigate to the root directory of the project and execute the following command:
python3 app.py
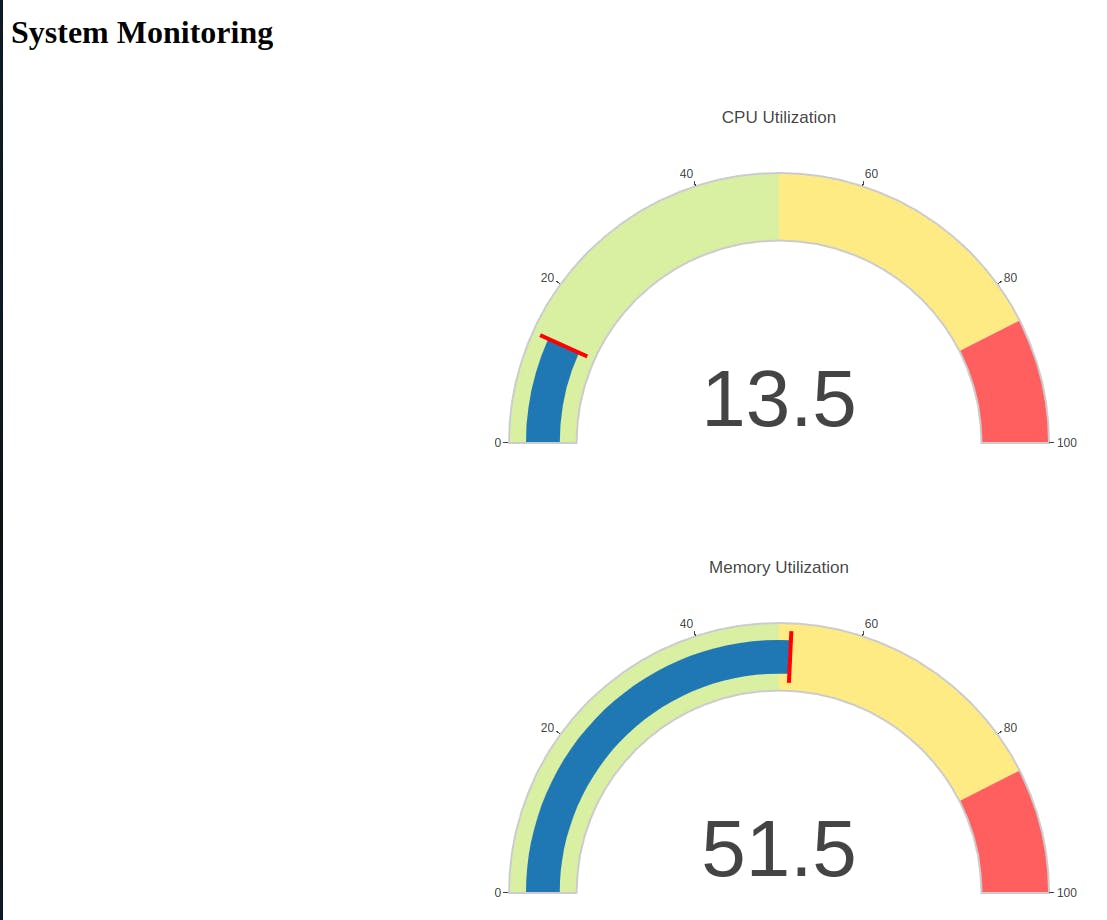
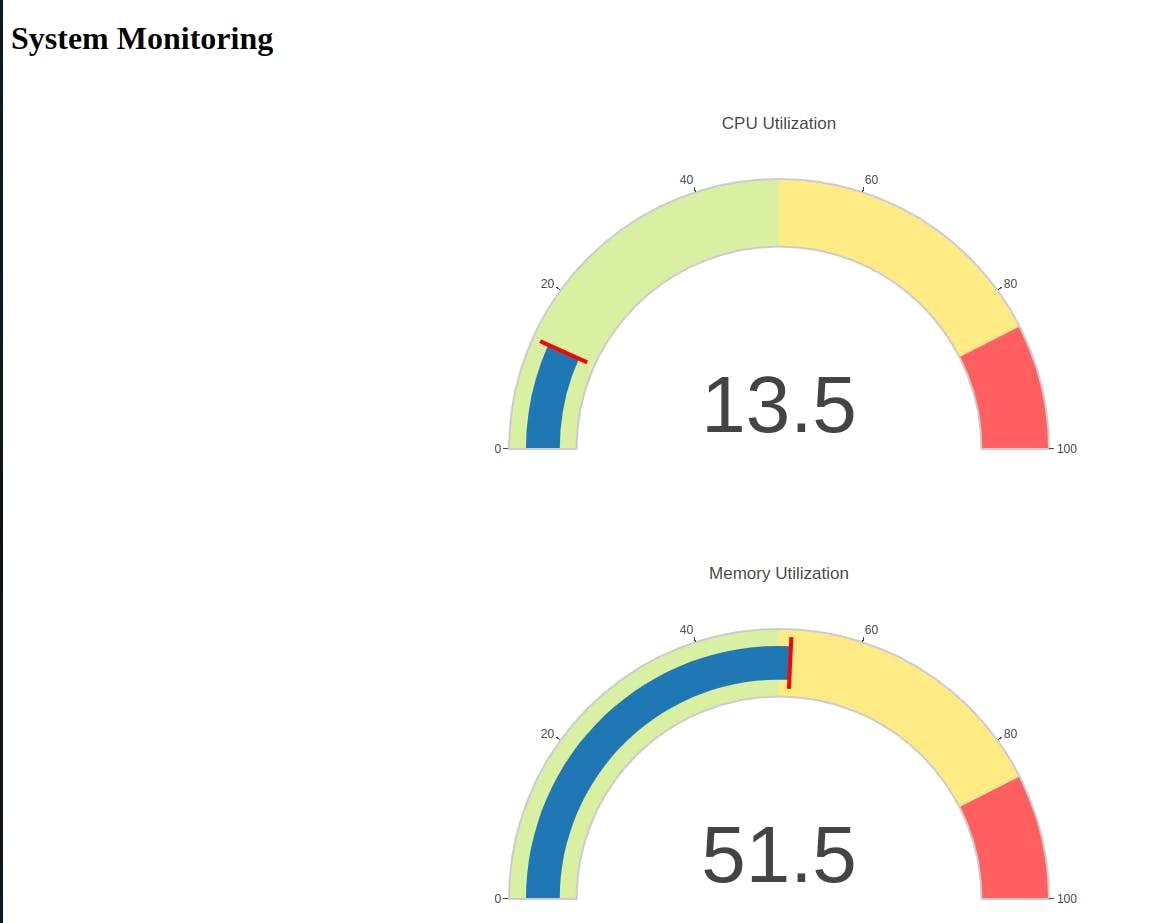
This will start the Flask server on localhost:5000. Navigate to http://localhost:5000/ on your browser to access the application.
Part 2: Dockerizing the Flask application
Step 1: Create a Dockerfile
Create a Dockerfile in the root directory of the project with the following contents:
# Use the official Python image as the base image
FROM python:3.11-buster
# Set the working directory in the container
WORKDIR /app
# Copy the requirements file to the working directory
COPY requirements.txt .
# Install the required Python packages
RUN pip3 install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# Copy the application code to the working directory
COPY . .
# Set the environment variables for the flask app
ENV FLASK_RUN_HOST=0.0.0.0
# Expose the port on which the flask app will run
EXPOSE 5000
# Start the flask app when the container is run
CMD ["flask","run"]
Step 2: Build the Docker image
To build the Docker image, execute the following command:
docker build -t <image_name> .
Step 3: Run the Docker container
To run the Docker container, execute the following command:
docker run -p 5000:5000 <image_name>
This will start the Flask server in a Docker container on localhost:5000. Navigate to http://localhost:5000/ on your browser to access the application.
Part 3: Pushing the Docker image to ECR
Step 1: Create an ECR repository
Create an ECR repository using Python:
Create a file ecr.py
import boto3
# Create an ECR client
ecr_client = boto3.client('ecr')
# Create a new ECR repository
repository_name = 'python-monitoring-app'
response = ecr_client.create_repository(repositoryName=repository_name)
# Print the repository URI
repository_uri = response['repository']['repositoryUri']
print(repository_uri)
Before running this file make sure you have configure your aws account with your local machine.
Run ecr.py
python3 ecr.py
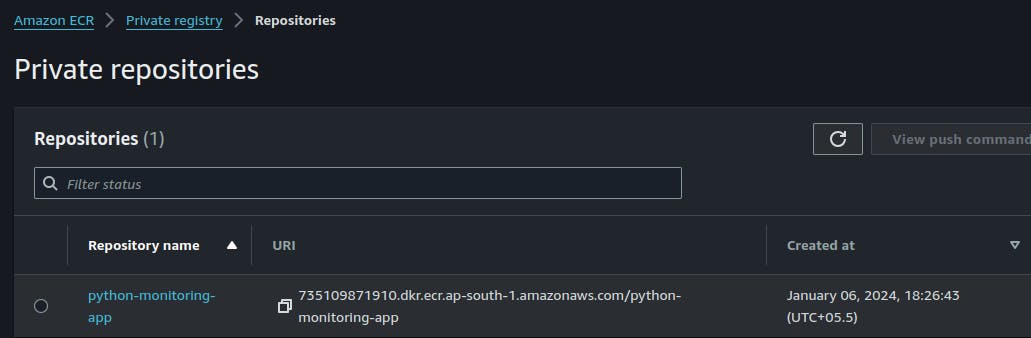
Step 2: Push the Docker image to ECR
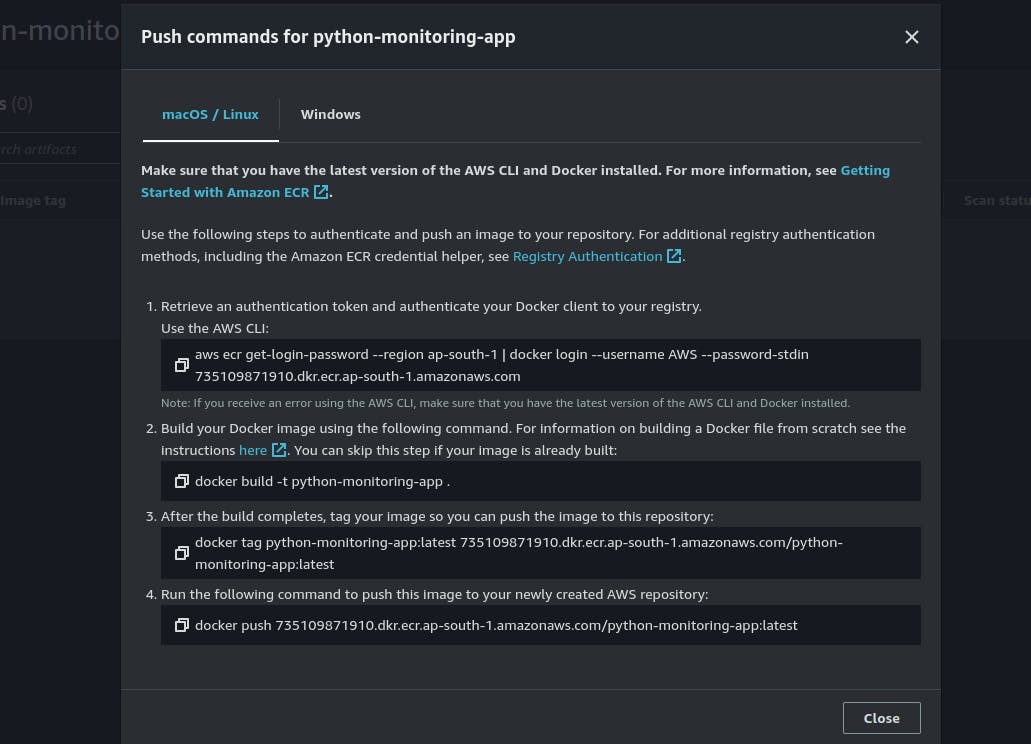
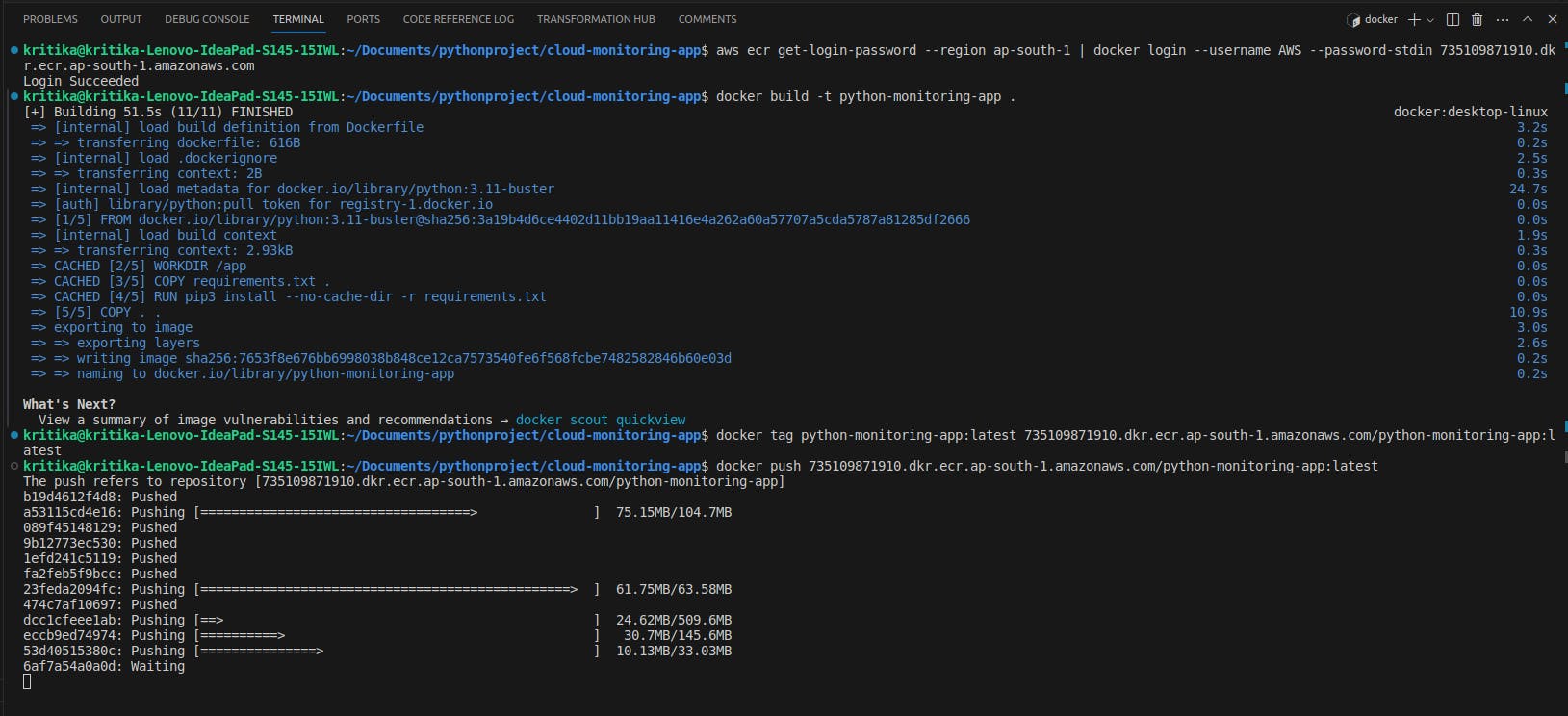
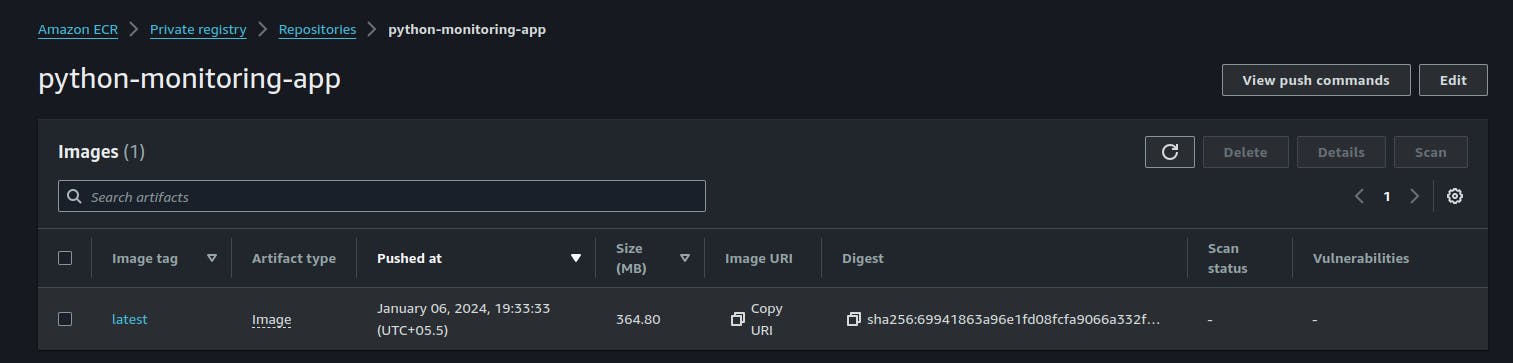
Push the Docker image to ECR using the push commands.
Part 4: Creating an EKS cluster and deploying the app using Python
Step 1: Create an EKS cluster
Create an EKS cluster and add node group
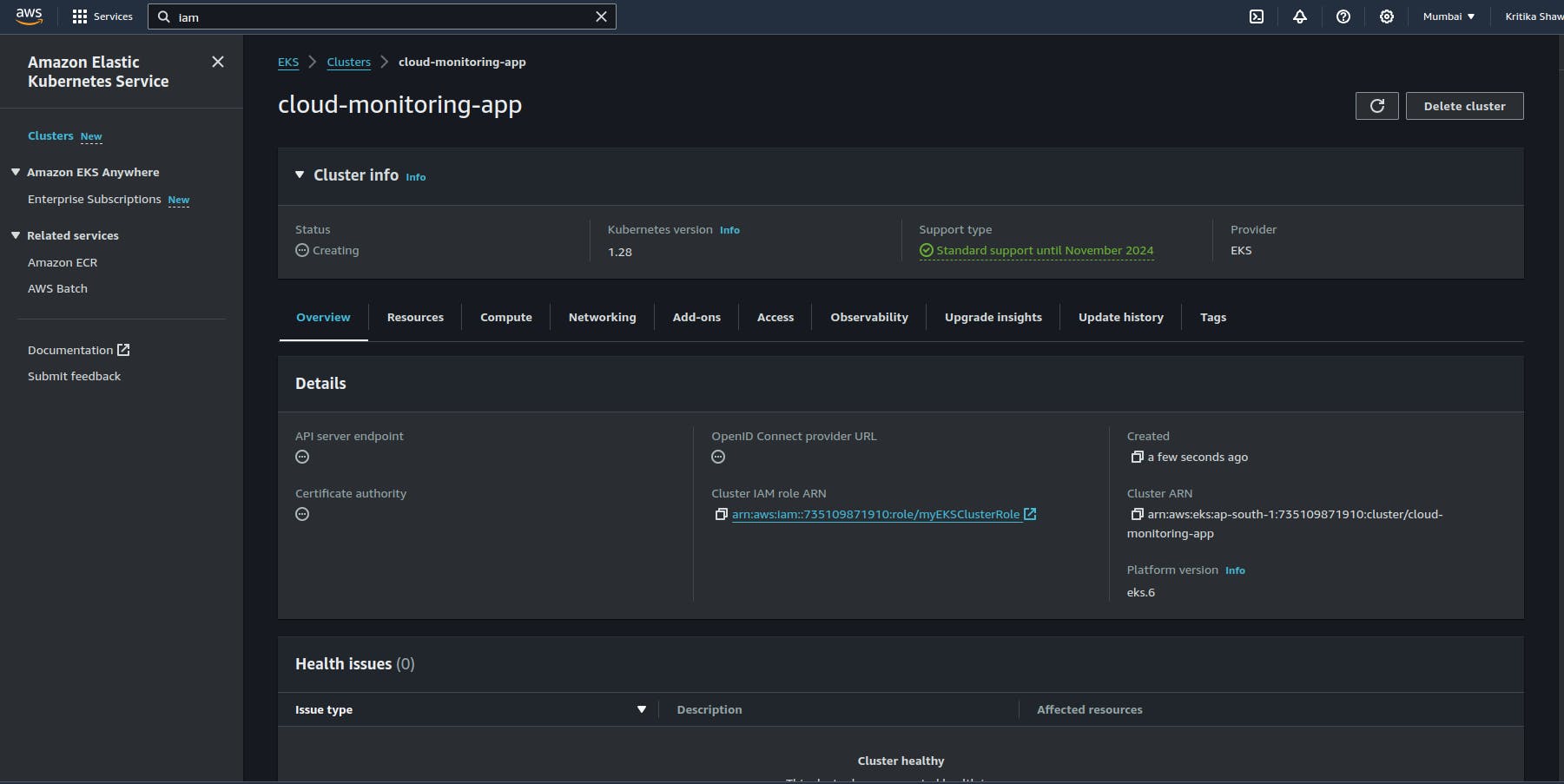
Step 2: Create a node group
Create a node group in the EKS cluster.
Step 3: Create deployment and service
from kubernetes import client, config
# Load Kubernetes configuration
config.load_kube_config()
# Create a Kubernetes API client
api_client = client.ApiClient()
# Define the deployment
deployment = client.V1Deployment(
metadata=client.V1ObjectMeta(name="my-flask-app"),
spec=client.V1DeploymentSpec(
replicas=1,
selector=client.V1LabelSelector(
match_labels={"app": "my-flask-app"}
),
template=client.V1PodTemplateSpec(
metadata=client.V1ObjectMeta(
labels={"app": "my-flask-app"}
),
spec=client.V1PodSpec(
containers=[
client.V1Container(
name="my-flask-container",
image="568373317874.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-cloud-native-repo:latest",
ports=[client.V1ContainerPort(container_port=5000)]
)
]
)
)
)
)
# Create the deployment
api_instance = client.AppsV1Api(api_client)
api_instance.create_namespaced_deployment(
namespace="default",
body=deployment
)
# Define the service
service = client.V1Service(
metadata=client.V1ObjectMeta(name="my-flask-service"),
spec=client.V1ServiceSpec(
selector={"app": "my-flask-app"},
ports=[client.V1ServicePort(port=5000)]
)
)
# Create the service
api_instance = client.CoreV1Api(api_client)
api_instance.create_namespaced_service(
namespace="default",
body=service
)
make sure to edit the name of the image on line 25 with your image Uri.
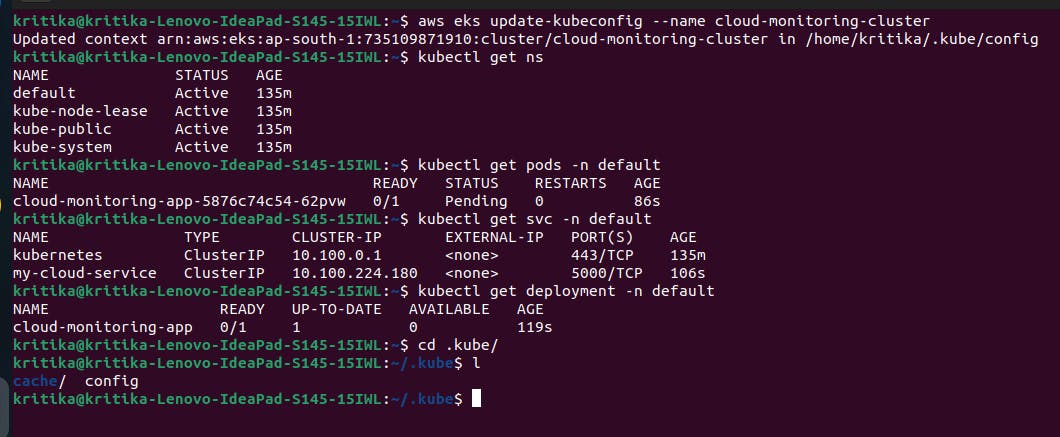
Once you run this file by running “python3 eks.py” deployment and service will be created.
Check by running following commands:
kubectl get deployment -n default (check deployments)
kubectl get service -n default (check service)
kubectl get pods -n default (to check the pods)
Once your pod is up and running, run the port-forward to expose the service
kubectl port-forward service/<service_name> 5000:5000
Thank you so much for taking the time to read till the end! Hope you found this blog informative and helpful.
Feel free to explore more of my content, and don't hesitate to reach out if need any assistance from me or in case of you have any questions.
Happy Learning!
~kritika :)
Connect with me: LinkedIn
